22nd anniversary of the ETFs industry in India
Press Release
London - (ETFGI) January 8, 2024 - Today marks the 22nd anniversary of the ETFs industry in India.
Benchmark Asset Management in India, founded in 2001 by Rajan Mehta and Sanjiv Shah, listed the first ETF in India called Nifty Bees ETF on January 8, 2022, on the National Stock Exchange (NSE). The ETF is now known as the Nippon India ETF Nifty Bank BEES ticker BBEES IN with US$782.77 million in assets under management on January 8, 2024.
Benchmark Asset Management was acquired by Goldman Sachs Asset Management in 2011. Reliance Capital Asset Management (RCAM) acquired Goldman Sachs’ mutual fund business in India, which included 12 ETFs, for approx. US$37.5 million in a cash deal on October 21, 2015.
Nippon Life Insurance acquired RCAM in two phases 1) in 2012, Nippon Life bought 26% stake in RCAM and 2) in 2015, Nippon Life increased its stake to 49%. Nippon India Mutual Fund acquired RCAM in October 2019, after Nippon Life Insurance of Japan completed the acquisition of 75% stake in Reliance Nippon Life Asset Management from Reliance Capital.
RCAM changed its name to Nippon India Mutual Fund on September 28, 2019. This was after Nippon Life Insurance of Japan completed the acquisition of 75% stake in Reliance Nippon Life Asset Management from Reliance Capital.
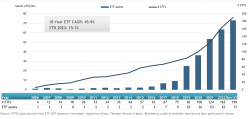
At the end of November 2023, the Indian ETF industry had 190 ETFs, assets of US$73 billion, from 19 providers listed on 2 exchanges, according to ETFGI.
SBI is the largest ETF provider in terms of assets with US$33 Bn (SBI Funds Management, is a joint venture between State Bank of India (SBI) and Amundi which owns a 36.8% stake), reflecting 45.5% market share; Nippon India MF is second with US$11 Bn and 15.4% market share, followed by UTI AM with US$10 Bn and 13.8% market share. The top three ETF providers, out of 19, account for 74.8% of Indian ETF assets.
Seventy percent of the ETFs and 67.6% of the assets invested in ETFs listed in India are tracking an index created by NSE Indices.
ETFs industry in India asset growth at end of November 2023

Regulatory changes to create a more level playing field for ETFs and the government supporting the development of ETF have helped the growth of the ETFs industry in India - the 10 year CAGR is: 45.9%. SEBI the Securities and Exchange Board of India, the regulator for the Indian securities market banned upfront commissions paid by Asset Management Companies (AMCs) to mutual fund distributors on October 22, 2018.
The Indian government has used ETFs to divest its share in public sector enterprises. Some of the ETFs that are based on the Indian government divesting holdings are:
CPSE ETF: tracks the Nifty CPSE Index, which consists of 12 CPSEs in which the government holds a stake. The CPSE ETF was launched in 2014.
Bharat 22 ETF: tracks the S&P BSE Bharat 22 Index, which comprises 22 companies from six sectors, including CPSEs (Central Public Sector Enterprises), public sector banks, and private sector firms. The Bharat 22 ETF was launched in 2017.
SBI ETF PSU Bank: tracks the Nifty PSU Bank Index, which measures the performance of public sector banks in India. The SBI ETF PSU Bank was launched in 2019.
We believe 2024 will see several new asset managers enter the ETFs industry in India.
Contact deborah.fuhr@etfgi.com if you have any questions or comments on the press release or ETFGI events, research or consulting services.
|
|


